CONCEPT RECAPITULATION TEST - I Paper 1
Question Paper
16 Pages
SAS
Contributed by
Srinivasan Aayushman Sood
Loading
 FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.comCONCEPT RECAPITULATION TEST - IPaper 1Time Allotted: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 180Please read the instructions carefully. You are allotted 5 minutesspecifically for this purpose. You are not allowed to leave the Examination Hall before the end ofthe test.INSTRUCTIONSA. General Instructions1. Attempt ALL the questions. Answers have to be marked on the OMR sheets.2. This question paper contains Three Parts.3. Part-I is Physics, Part-II is Chemistry and Part-III is Mathematics.4. Each part is further divided into two sections: Section-A & Section-C5. Rough spaces are provided for rough work inside the question paper. No additional sheets will beprovided for rough work.6. Blank Papers, clip boards, log tables, slide rule, calculator, cellular phones, pagers and electronicdevices, in any form, are not allowed.B. Filling of OMR Sheet1. Ensure matching of OMR sheet with the Question paper before you start marking your answerson OMR sheet.2. On the OMR sheet, darken the appropriate bubble with black pen for each character of yourEnrolment No. and write your Name, Test Centre and other details at the designated places.3. OMR sheet contains alphabets, numerals & special characters for marking answers.C. Marking Scheme For All Three Parts.(i) Section-A (01 to 10) contains 10 multiple choice questions which have only one correct answer.Each question carries +2 marks for correct answer. There is no negative marking.Section-A (11 to 15) contains 5 multiple choice questions which have more than one correctanswer. Each question carries +4 marks for correct answer and – 1 mark for wrong answer.(ii) Section-C (01 to 05) contains 5 Numerical based questions with answers as numerical valueand each question carries +4 marks for correct answer and – 1 mark for wrong answer.Name of the CandidateEnrolment No.ALL INDIA TEST SERIESFIITJEEJEE (Advanced), 2014From Classroom/Integrated School Programs7 in Top 20, 23 in Top 100, 54 in Top 300, 106 in Top 500 All India Ranks & 2314 Students from Classroom/Integrated School Programs & 3723 Students from All Programs have been Awarded a Rank in JEE (Advanced), 2013
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.comCONCEPT RECAPITULATION TEST - IPaper 1Time Allotted: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 180Please read the instructions carefully. You are allotted 5 minutesspecifically for this purpose. You are not allowed to leave the Examination Hall before the end ofthe test.INSTRUCTIONSA. General Instructions1. Attempt ALL the questions. Answers have to be marked on the OMR sheets.2. This question paper contains Three Parts.3. Part-I is Physics, Part-II is Chemistry and Part-III is Mathematics.4. Each part is further divided into two sections: Section-A & Section-C5. Rough spaces are provided for rough work inside the question paper. No additional sheets will beprovided for rough work.6. Blank Papers, clip boards, log tables, slide rule, calculator, cellular phones, pagers and electronicdevices, in any form, are not allowed.B. Filling of OMR Sheet1. Ensure matching of OMR sheet with the Question paper before you start marking your answerson OMR sheet.2. On the OMR sheet, darken the appropriate bubble with black pen for each character of yourEnrolment No. and write your Name, Test Centre and other details at the designated places.3. OMR sheet contains alphabets, numerals & special characters for marking answers.C. Marking Scheme For All Three Parts.(i) Section-A (01 to 10) contains 10 multiple choice questions which have only one correct answer.Each question carries +2 marks for correct answer. There is no negative marking.Section-A (11 to 15) contains 5 multiple choice questions which have more than one correctanswer. Each question carries +4 marks for correct answer and – 1 mark for wrong answer.(ii) Section-C (01 to 05) contains 5 Numerical based questions with answers as numerical valueand each question carries +4 marks for correct answer and – 1 mark for wrong answer.Name of the CandidateEnrolment No.ALL INDIA TEST SERIESFIITJEEJEE (Advanced), 2014From Classroom/Integrated School Programs7 in Top 20, 23 in Top 100, 54 in Top 300, 106 in Top 500 All India Ranks & 2314 Students from Classroom/Integrated School Programs & 3723 Students from All Programs have been Awarded a Rank in JEE (Advanced), 2013Page 1
 AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com2Useful DataPHYSICSAcceleration due to gravity g = 10 m/s2Planck constant h = 6.6 1034J-sCharge of electron e = 1.6 1019CMass of electron me= 9.1 1031kgPermittivity of free space 0= 8.85 1012C2/N-m2Density of water water= 103kg/m3Atmospheric pressure Pa= 105N/m2Gas constant R = 8.314 J K1mol1CHEMISTRYGas Constant R = 8.314 J K1mol1= 0.0821 Lit atm K1mol1= 1.987 2 Cal K1mol1Avogadro's Number Na= 6.023 1023Planck’s constant h = 6.625 1034Js= 6.625 10–27ergs1 Faraday = 96500 coulomb1 calorie = 4.2 joule1 amu = 1.66 10–27kg1 eV = 1.6 10–19JAtomic No: H=1, He = 2, Li=3, Be=4, B=5, C=6, N=7, O=8,N=9, Na=11, Mg=12, Si=14, Al=13, P=15, S=16,Cl=17, Ar=18, K =19, Ca=20, Cr=24, Mn=25,Fe=26, Co=27, Ni=28, Cu = 29, Zn=30, As=33,Br=35, Ag=47, Sn=50, I=53, Xe=54, Ba=56,Pb=82, U=92.Atomic masses: H=1, He=4, Li=7, Be=9, B=11, C=12, N=14, O=16,F=19, Na=23, Mg=24, Al = 27, Si=28, P=31, S=32,Cl=35.5, K=39, Ca=40, Cr=52, Mn=55, Fe=56, Co=59,Ni=58.7, Cu=63.5, Zn=65.4, As=75, Br=80, Ag=108,Sn=118.7, I=127, Xe=131, Ba=137, Pb=207, U=238.
AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com2Useful DataPHYSICSAcceleration due to gravity g = 10 m/s2Planck constant h = 6.6 1034J-sCharge of electron e = 1.6 1019CMass of electron me= 9.1 1031kgPermittivity of free space 0= 8.85 1012C2/N-m2Density of water water= 103kg/m3Atmospheric pressure Pa= 105N/m2Gas constant R = 8.314 J K1mol1CHEMISTRYGas Constant R = 8.314 J K1mol1= 0.0821 Lit atm K1mol1= 1.987 2 Cal K1mol1Avogadro's Number Na= 6.023 1023Planck’s constant h = 6.625 1034Js= 6.625 10–27ergs1 Faraday = 96500 coulomb1 calorie = 4.2 joule1 amu = 1.66 10–27kg1 eV = 1.6 10–19JAtomic No: H=1, He = 2, Li=3, Be=4, B=5, C=6, N=7, O=8,N=9, Na=11, Mg=12, Si=14, Al=13, P=15, S=16,Cl=17, Ar=18, K =19, Ca=20, Cr=24, Mn=25,Fe=26, Co=27, Ni=28, Cu = 29, Zn=30, As=33,Br=35, Ag=47, Sn=50, I=53, Xe=54, Ba=56,Pb=82, U=92.Atomic masses: H=1, He=4, Li=7, Be=9, B=11, C=12, N=14, O=16,F=19, Na=23, Mg=24, Al = 27, Si=28, P=31, S=32,Cl=35.5, K=39, Ca=40, Cr=52, Mn=55, Fe=56, Co=59,Ni=58.7, Cu=63.5, Zn=65.4, As=75, Br=80, Ag=108,Sn=118.7, I=127, Xe=131, Ba=137, Pb=207, U=238.Page 2
 AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com3PPhhyyssiiccss PART – ISECTION – ASingle Correct Choice TypeThis section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D)out of which ONLY ONE is correct.1. Two balls are dropped from the same point after an interval of 1 second. Their separation 3second after the release of the second ball. (g = 10 m/s2)(A) 25 m (B) 30 m(C) 35 m (D) 40 m2. The upper half of an inclined plane of inclination is perfectly smooth while the lower half isrough. A block starting from rest at the top of the plane will come to rest at the bottom if thecoefficient of friction between the block and the lower half of the plane is(A) = 2 tan (B) = tan (C)2tan (D)1tan 3. A spring is compressed between two blocks of masses m1and m2placed on a horizontalfrictionless surface. When the blocks are released. The blocks travel distance x1and x2respectively before coming to rest. The ratio x1/x2is(A) m1/m2(B) m2/m1(C)12mm(D)21mm4. If A is the areal velocity of planet of mass M, its angular momentum is(A) M (B) 2MA(C) A2M (D) AM25. A meteor of mass M breaks up into two parts. The mass of one part is m. For a given separation rthe mutual gravitational force between the two parts will be maximum if(A) m = (M/2) (B) m = (M/3)(C) m =M2(D)Mm2 2Space for Rough work
AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com3PPhhyyssiiccss PART – ISECTION – ASingle Correct Choice TypeThis section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D)out of which ONLY ONE is correct.1. Two balls are dropped from the same point after an interval of 1 second. Their separation 3second after the release of the second ball. (g = 10 m/s2)(A) 25 m (B) 30 m(C) 35 m (D) 40 m2. The upper half of an inclined plane of inclination is perfectly smooth while the lower half isrough. A block starting from rest at the top of the plane will come to rest at the bottom if thecoefficient of friction between the block and the lower half of the plane is(A) = 2 tan (B) = tan (C)2tan (D)1tan 3. A spring is compressed between two blocks of masses m1and m2placed on a horizontalfrictionless surface. When the blocks are released. The blocks travel distance x1and x2respectively before coming to rest. The ratio x1/x2is(A) m1/m2(B) m2/m1(C)12mm(D)21mm4. If A is the areal velocity of planet of mass M, its angular momentum is(A) M (B) 2MA(C) A2M (D) AM25. A meteor of mass M breaks up into two parts. The mass of one part is m. For a given separation rthe mutual gravitational force between the two parts will be maximum if(A) m = (M/2) (B) m = (M/3)(C) m =M2(D)Mm2 2Space for Rough workPage 3
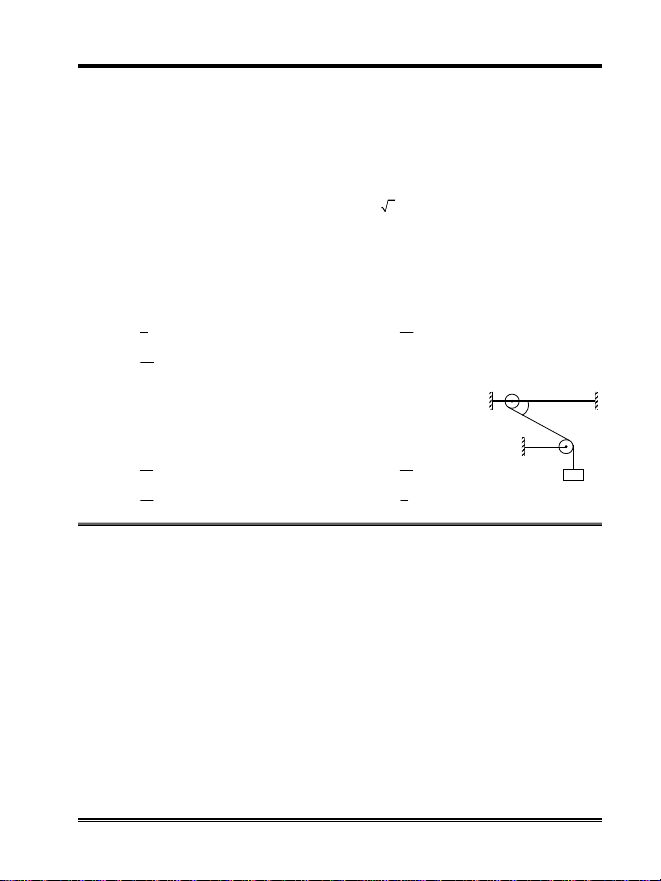 AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com46. A wire breaks when subjected to a stress S. If is the density of the material of the wire and g,the acceleration due to gravity, then the length of the wire so that it breaks by its own weight is(A) gs (B) g/s(C) gs/ (D) s/g7. A cylinder has a radius r. To what height h should it be filled with water so that the thrust on itswalls is equal to that on its bottom(A) h = 2r (B) h = r(C) h = (r/2) (D) h = (r/4)8 A swimmer can swim in still water with a speed of5m/s. While crossing a river his averagespeed is 3 m/s. If he cross the river in the shortest possible time, what is the speed of flow ofwater?(A) 2 m/s (B) 4 m/s(C) 6 m/s (D) 8 m/s9 A car starting from rest is accelerated at constant rate until it attains a constant speed v. It is thenretarded at a constant rate until it comes to rest. Considering that the car moves with constantspeed for half of the time of total journey, the average speed of the car for the journey is(A)v4(B)3v4(C)3v2(D) Data insufficient10. A smooth ring P of mass m can slide on a fixed horizontal rod. A stringtied to the ring passes over a fixed pulley and carries a block Q of mass(m/2) as shown in the figure. At an instant, the string between the ringand the pulley makes an angle 60 with the rod.The initial acceleration of the ring is(A)2g3(B)2g6(C)2g9(D)g360mPQm/2Space for Rough work
AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com46. A wire breaks when subjected to a stress S. If is the density of the material of the wire and g,the acceleration due to gravity, then the length of the wire so that it breaks by its own weight is(A) gs (B) g/s(C) gs/ (D) s/g7. A cylinder has a radius r. To what height h should it be filled with water so that the thrust on itswalls is equal to that on its bottom(A) h = 2r (B) h = r(C) h = (r/2) (D) h = (r/4)8 A swimmer can swim in still water with a speed of5m/s. While crossing a river his averagespeed is 3 m/s. If he cross the river in the shortest possible time, what is the speed of flow ofwater?(A) 2 m/s (B) 4 m/s(C) 6 m/s (D) 8 m/s9 A car starting from rest is accelerated at constant rate until it attains a constant speed v. It is thenretarded at a constant rate until it comes to rest. Considering that the car moves with constantspeed for half of the time of total journey, the average speed of the car for the journey is(A)v4(B)3v4(C)3v2(D) Data insufficient10. A smooth ring P of mass m can slide on a fixed horizontal rod. A stringtied to the ring passes over a fixed pulley and carries a block Q of mass(m/2) as shown in the figure. At an instant, the string between the ringand the pulley makes an angle 60 with the rod.The initial acceleration of the ring is(A)2g3(B)2g6(C)2g9(D)g360mPQm/2Space for Rough workPage 4
 AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com5Multiple Correct Answer(s) TypeThis section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) forits answer, out of which ONE OR MORE is/are correct.11. A particle having mass m and positive charge q whirls along vertical circle of radius R. At thecentre of circle, another positive charge 2q is fixed.(A) The minimum velocity given at the lowest point to complete vertical circular motion is lessthan5gRfor motion in gravity.(B) For any value of velocity given in horizontal direction at the lowest point in gravity free space itwill perform vertical circular motion.(C) Tension in gravity free space cannot becomes zero at any point during motion.(D) If the charge at the centre is removed and considering the motion in gravity tension will alsobe function of charge on particle.12. The potential energy of a particle of mass 0.1 kg, moving along the x-axis, is given byU = 5x(x4)J, where x is in meters. It can be concluded that(A) The particle is acted upon by a variable force.(B) The minimum potential energy during motion is 20 J(C) The speed of the particle is maximum at x = 2m.(D) The period of oscillation of the particle is (/5) sec.Space for Rough work
AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com5Multiple Correct Answer(s) TypeThis section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) forits answer, out of which ONE OR MORE is/are correct.11. A particle having mass m and positive charge q whirls along vertical circle of radius R. At thecentre of circle, another positive charge 2q is fixed.(A) The minimum velocity given at the lowest point to complete vertical circular motion is lessthan5gRfor motion in gravity.(B) For any value of velocity given in horizontal direction at the lowest point in gravity free space itwill perform vertical circular motion.(C) Tension in gravity free space cannot becomes zero at any point during motion.(D) If the charge at the centre is removed and considering the motion in gravity tension will alsobe function of charge on particle.12. The potential energy of a particle of mass 0.1 kg, moving along the x-axis, is given byU = 5x(x4)J, where x is in meters. It can be concluded that(A) The particle is acted upon by a variable force.(B) The minimum potential energy during motion is 20 J(C) The speed of the particle is maximum at x = 2m.(D) The period of oscillation of the particle is (/5) sec.Space for Rough workPage 5
 AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com613. A cubical block is floating in a liquid with one third of it’s volume immersed in the liquid. When thewhole system accelerates upwards with acceleration of g/2.(A) The fraction of volume immersed in the liquid will change.(B) The buoyancy force on the block will change.(C) The buoyancy force will increase by 50 percent.(D) The pressure in the liquid will increased.14. Two concentric metallic shell’s of radius R and 2R, out of which the inner shell is having charge Qand outer shell is uncharged. If they are connected with a conducting wire. Then,(A) Q amount of charge will flow from inner to outer shell.(B) Q/e number of electrons will flow from outer to inner shell, where e charge on electron.(C)2KQ4Ramount of heat is produced in the wire(D)2KQ2Ramount of heat is produced in the wire.15. A sound wave of frequency n travels horizontally to the right. It is reflected from a large verticalplane surface moving to the left with a speed v. The speed of sound in the medium is c. Then,(A) The number of waves striking the surface pre second isn(c v)c.(B) The frequency of the reflected wave isn(c v)(c v)(C) The wavelength of the reflected wave isc(c v)n(c v)(D) The number of beats heard by a stationary listener to the left of the reflecting surface isnvc vSpace for Rough work
AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com613. A cubical block is floating in a liquid with one third of it’s volume immersed in the liquid. When thewhole system accelerates upwards with acceleration of g/2.(A) The fraction of volume immersed in the liquid will change.(B) The buoyancy force on the block will change.(C) The buoyancy force will increase by 50 percent.(D) The pressure in the liquid will increased.14. Two concentric metallic shell’s of radius R and 2R, out of which the inner shell is having charge Qand outer shell is uncharged. If they are connected with a conducting wire. Then,(A) Q amount of charge will flow from inner to outer shell.(B) Q/e number of electrons will flow from outer to inner shell, where e charge on electron.(C)2KQ4Ramount of heat is produced in the wire(D)2KQ2Ramount of heat is produced in the wire.15. A sound wave of frequency n travels horizontally to the right. It is reflected from a large verticalplane surface moving to the left with a speed v. The speed of sound in the medium is c. Then,(A) The number of waves striking the surface pre second isn(c v)c.(B) The frequency of the reflected wave isn(c v)(c v)(C) The wavelength of the reflected wave isc(c v)n(c v)(D) The number of beats heard by a stationary listener to the left of the reflecting surface isnvc vSpace for Rough workPage 6
 AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com7SECTION –CInteger Answer TypeThis section contains 5 questions. The answer to each question is a single digit integer, ranging from 0to 9 (both inclusive).1. A glass sphere having refractive index (3/2) is having a smallirregularity at its centre. It is placed in a liquid of refractive index34such that surface of liquid is r high above sphere where r isradius of sphere. If irregularity is viewed from above normally, thedistance is 26/K cm from centre where eye will observe theirregularity. Then find the value of K. (r = 20 cm)r=3/2r=4/32. Two block of masses m and M are connected by means of a metal wire passing over africtionless fixed pulley. The area of cross-section of the wire is 6.5 109m2and its breakingstress is 2 109Nm2. If m = 1 kg, if the maximum value of M is K 1.86 kg for which the wire willnot break. Find the value of K. (g = 10 m/s2)3. A small cubical block of mass 1 kg is placed inside a rough rectangulargroove12 made in a circular table as shown in the figure. The tablestarts rotating with angular acceleration 1 rad/sec2in a horizontal planeabout its axis. The time is10 Ksec after which the blocks will start motionwith respect to table. Find the value of K. (Take g = 10 m/s2) Assume thesize of block slightly smaller then the width of groove.4 cm3 cm4. Two particles of mass M = 3 kg each are kept on a horizontal circular platform on two mutuallyperpendicular radii at equal distance R = 1 m from the centre of the table. The particles areconnected with a string, which is just taught when the platform is not rotating. Coefficient offriction between the platform and block is = 0.1. Then the maximum angular speed ( inrad/sec) of platform about its centre so that the blocks remain stationary relative to platform. (takeg = 10 m/s2)5. A uniform cylinder of radius R(= 3m) is spin about its axis at an angularvelocity 0(= 40rad/sec) and placed between two perpendicular wall.The coefficient of friction between the walls and cylinder is ( = 2). Then,25 K turns will the cylinder make before it stops. Find the value of K.Space for Rough work
AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com7SECTION –CInteger Answer TypeThis section contains 5 questions. The answer to each question is a single digit integer, ranging from 0to 9 (both inclusive).1. A glass sphere having refractive index (3/2) is having a smallirregularity at its centre. It is placed in a liquid of refractive index34such that surface of liquid is r high above sphere where r isradius of sphere. If irregularity is viewed from above normally, thedistance is 26/K cm from centre where eye will observe theirregularity. Then find the value of K. (r = 20 cm)r=3/2r=4/32. Two block of masses m and M are connected by means of a metal wire passing over africtionless fixed pulley. The area of cross-section of the wire is 6.5 109m2and its breakingstress is 2 109Nm2. If m = 1 kg, if the maximum value of M is K 1.86 kg for which the wire willnot break. Find the value of K. (g = 10 m/s2)3. A small cubical block of mass 1 kg is placed inside a rough rectangulargroove12 made in a circular table as shown in the figure. The tablestarts rotating with angular acceleration 1 rad/sec2in a horizontal planeabout its axis. The time is10 Ksec after which the blocks will start motionwith respect to table. Find the value of K. (Take g = 10 m/s2) Assume thesize of block slightly smaller then the width of groove.4 cm3 cm4. Two particles of mass M = 3 kg each are kept on a horizontal circular platform on two mutuallyperpendicular radii at equal distance R = 1 m from the centre of the table. The particles areconnected with a string, which is just taught when the platform is not rotating. Coefficient offriction between the platform and block is = 0.1. Then the maximum angular speed ( inrad/sec) of platform about its centre so that the blocks remain stationary relative to platform. (takeg = 10 m/s2)5. A uniform cylinder of radius R(= 3m) is spin about its axis at an angularvelocity 0(= 40rad/sec) and placed between two perpendicular wall.The coefficient of friction between the walls and cylinder is ( = 2). Then,25 K turns will the cylinder make before it stops. Find the value of K.Space for Rough workPage 7
 AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com8CChheemmiissttrryyPART – IISECTION – ASingle Correct Choice TypeThis section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D)out of which ONLY ONE is correct.1. Which of the following reactions product is correct, correspondingly?(A)CH3HClBrAlc. KOHClCH3major(B)CH N OACCNOAC(C)OACOAC OACACOH(D)CH CH2 2CH N2.O2NH OHHCl?The major product of the following reaction is.....?(A)Cl(B)NOH(C)NO(D)NOHSpace for Rough work
AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com8CChheemmiissttrryyPART – IISECTION – ASingle Correct Choice TypeThis section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D)out of which ONLY ONE is correct.1. Which of the following reactions product is correct, correspondingly?(A)CH3HClBrAlc. KOHClCH3major(B)CH N OACCNOAC(C)OACOAC OACACOH(D)CH CH2 2CH N2.O2NH OHHCl?The major product of the following reaction is.....?(A)Cl(B)NOH(C)NO(D)NOHSpace for Rough workPage 8
 AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com93. What is the correct order of basic strength of the following amines?NO2NO2Me2N(I)NH2(II)NN NHHH(III) (IV)NCH3(A) (II) > (IV) > (III) > (I) (B) (IV) > (I) > (III) > (II)(C) (IV) > (I) > (II) > (III) (D) (III) > (IV) > (II) > (I)4. The complex [Fe(H2O)5(NO)]2+is formed in the ring test for nitrate when freshly prepared FeSO4solution is added to aqueous solution of3NOfollowed by addition of conc. H2SO4. The complexis formed by charge transfer, which of the following change occurs?(A)3 2Fe Fe ; NO NO (B)2 3Fe Fe ; NO NO (C)2Fe Fe ; NO NO (D)2 3Fe Fe ; NO NO 5.CHCH3OCH2CH3CH35PCl3CH Cl A (A) CH3Cl is formed by SN1 process.(B) CH3Cl is formed by SN2 process(C) A isCH3CHCH2CH3Cl,which is formed by SN2 process(D) A isCH3CHCH2CH3Cl, which is formed by SN1 process6. For the following equilibria in a close container5 3 2PCl g PCl g Cl gAt a constant temperature, the volume of the container is halved suddenly. Which of the followingis correct for Kpand ?(A) Both Kpand changes (B) None of the Kpand change(C) Kpchanges but does not (D) - changes but Kpdoes notSpace for Rough work
AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com93. What is the correct order of basic strength of the following amines?NO2NO2Me2N(I)NH2(II)NN NHHH(III) (IV)NCH3(A) (II) > (IV) > (III) > (I) (B) (IV) > (I) > (III) > (II)(C) (IV) > (I) > (II) > (III) (D) (III) > (IV) > (II) > (I)4. The complex [Fe(H2O)5(NO)]2+is formed in the ring test for nitrate when freshly prepared FeSO4solution is added to aqueous solution of3NOfollowed by addition of conc. H2SO4. The complexis formed by charge transfer, which of the following change occurs?(A)3 2Fe Fe ; NO NO (B)2 3Fe Fe ; NO NO (C)2Fe Fe ; NO NO (D)2 3Fe Fe ; NO NO 5.CHCH3OCH2CH3CH35PCl3CH Cl A (A) CH3Cl is formed by SN1 process.(B) CH3Cl is formed by SN2 process(C) A isCH3CHCH2CH3Cl,which is formed by SN2 process(D) A isCH3CHCH2CH3Cl, which is formed by SN1 process6. For the following equilibria in a close container5 3 2PCl g PCl g Cl gAt a constant temperature, the volume of the container is halved suddenly. Which of the followingis correct for Kpand ?(A) Both Kpand changes (B) None of the Kpand change(C) Kpchanges but does not (D) - changes but Kpdoes notSpace for Rough workPage 9
 AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com107. Aluminum chloride exists as a dimer2 6Al Clin solid state as well as in solution of non-polarsolvents such as C6H6. When dissolved in water, it gives(A)2 36Al O HCl (B) 263Al H O Cl (C) 36Al OH 6HCl (D)33Al Cl 8. Resonance Energy of Toluene is 37.5 kcal/mol while that of Benzene is 36 kcal/mole then whichof the following explains this difference(A) Zeeman effect (B) Electromeric effect(C) Hyper-conjugation (D) – I effect9. The ortho and para-hydrogens possess:(A) Same physical properties but different chemical properties.(B) Different physical properties but same chemical properties.(C) Same chemical and physical properties.(D) Different physical and chemical properties.10. During extraction of Fe(A) Carbon is ultimately converted to CO2in combustion zone in blast furnace.(B) CO2is one of the by-products of reduction zone of blast furnace.(C) Cast iron is obtained from blast furnace.(D) Uppermost zone of blast furnace is slag formation zone.Space for Rough work
AITS-CRT-I (Paper-1)-PCM-JEE(Advanced)/14FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942website: www.fiitjee.com107. Aluminum chloride exists as a dimer2 6Al Clin solid state as well as in solution of non-polarsolvents such as C6H6. When dissolved in water, it gives(A)2 36Al O HCl (B) 263Al H O Cl (C) 36Al OH 6HCl (D)33Al Cl 8. Resonance Energy of Toluene is 37.5 kcal/mol while that of Benzene is 36 kcal/mole then whichof the following explains this difference(A) Zeeman effect (B) Electromeric effect(C) Hyper-conjugation (D) – I effect9. The ortho and para-hydrogens possess:(A) Same physical properties but different chemical properties.(B) Different physical properties but same chemical properties.(C) Same chemical and physical properties.(D) Different physical and chemical properties.10. During extraction of Fe(A) Carbon is ultimately converted to CO2in combustion zone in blast furnace.(B) CO2is one of the by-products of reduction zone of blast furnace.(C) Cast iron is obtained from blast furnace.(D) Uppermost zone of blast furnace is slag formation zone.Space for Rough workPage 10
Download this file to view remaining 6 pages
Related documents:
- Basics Economics Studies MCQs - MCQ
- Modern India –II Unit 3 Questions with answers - Question Bank
- Public Administration (Paper II) 2019 Question Paper - Question Paper
- Trigonometry (Solved MCQs and Notes) - Notes
- Managerial Economics (Syllabus)
- Basic Electronics and Computer Fundamentals MCQs - MCQ
- Zoology (Paper I) 2017 Question Paper - Question Paper
- INSTRUMENTS IN INTERNATIONAL FINACIAL MARKETS - INTERNATIONAL FINANCE - Notes
- PH8151 ENGINEERING PHYSICS QPaper Jan 2018 - Question Paper
- FULL TEST – I Paper-2 [ANSWERS, HINTS & SOLUTIONS]
- COMMODITIES MARKET - STOCK AND COMMODITY MARKET - Notes
- Experimental Skills Notes and MCQs - Notes
- Sanskrit - Prose,Vrutha,Alankara,Theories of Poetics & Grammar MCQs - MCQ
- BANKER AND THE CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP AND TYPES OF ACCOUNT HOLDERS - Banking regulation and operations (BRO) - Notes
- QP IFSM-23 GENERAL KNOWLEDGE - Question Paper
- UPSC 2021 Prelims ENVIRONMENT Answer Key with Explanation - Question Bank
- Sociology (Paper I) 2021 Question Paper - MCQ
- Office Management in Government MCQs with ansers - MCQ
- Titre préliminaire chapitre 2 - Question Paper
- Marketing-Management-II - MCQ
